Although the mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, studies involving structurally related drugs suggest that presynaptic binding of pregabalin to voltage-gated calcium channels is key to the antiseizure and antinociceptive effects observed in animal models. By binding presynaptically to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, pregabalin modulates the release of several excitatory neurotransmitters including glutamate, substance-P, norepinephrine, and calcitonin gene related peptide. In addition, pregabalin prevents the alpha2-delta subunit from being trafficked from the dorsal root ganglia to the spinal dorsal horn, which may also contribute to the mechanism of action. Although pregabalin is a structural derivative of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind directly to GABA or benzodiazepine receptors
| Cas No : | 148553-50-8 |
|---|---|
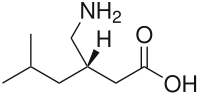
| Name : | Pregabalin |
| Synonyms : | (3S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid |
| Molecular Formula : | C8H17NO2 |
| Melting Point : | 194-196°C |
| Boiling Point : | 274 °C |
| Molecular Weight : | 159.23 g/mol |
| Density : | 0.997±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Solubility : | Freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic solutions |

Advancing global health through high-quality APIs, intermediates, and surgical products. Trusted solutions driven by innovation, quality, and care.





Copyright © 2025 Healnith Pharmaceuticals All rights reserved.